Preface ...................................................... xiii
Introduction .................................................... 1
Part 1. Background on Groups, Complexity, and Cryptography
Chapter 1. Background on Public-Key Cryptography ................ 7
1.1 Prom key establishment to encryption ....................... 8
1.2 The Diffie-Hellman key establishment ....................... 8
1.3 The ElGamal cryptosystem ................................... 9
1.4 The RS A cryptosystem ..................................... 10
1.5 Rabin's cryptosystem ...................................... 11
1.6 Authentication ............................................ 11
1.6.1. The Feige-Fiat-Shamir scheme ............................ 12
Chapter 2. Background on Combinatorial Group Theory ............ 13
2.1 Basic definitions and notation ............................ 13
2.2 Presentations of groups by generators and relators ........ 14
2.3 Algorithmic problems of group theory: decision, witness,
search .................................................... 15
2.3.1 The word problem ................................... 15
2.3.2 The conjugacy problem .............................. 16
2.3.3 The decomposition and factorization problems ....... 16
2.3.4 The membership problem ............................. 17
2.3.5 The isomorphism problem ............................ 17
2.3.6 More on search/witness problems .................... 18
2.4 Nielsen's and Schreier's methods .......................... 20
2.5 Tietze's method ........................................... 21
2.6 Normal forms .............................................. 22
Chapter 3. Background on Computational Complexity .............. 25
3.1 Algorithms ................................................ 25
3.1.1 Deterministic Turing machines ...................... 25
3.1.2 Non-deterministic Turing machines .................. 26
3.1.3 Probabilistic Turing machines ...................... 26
3.2 Computational problems .................................... 26
3.2.1 Decision and search computational problems ......... 27
3.2.2 Size functions ..................................... 28
3.2.1 Stratification ..................................... 30
3.2.4 Reductions and complete problems ................... 31
3.2.5 Many-to-one reductions ............................. 31
3.2.6 Turing reductions .................................. 31
3.3 The worst case complexity ................................. 32
3.3.1 Complexity classes ................................. 32
3.3.2 Class NP ........................................... 33
3.3.3 Polynomial-time many-to-one reductions and class
NP ................................................. 34
3.3.4 NP-complete problems ............................... 35
3.3.5 Deficiency of the worst case complexity ............ 37
Part 2. Non-commutative Cryptography
Chapter 4 Canonical Non-commutative Cryptography .............. 41
4.1 Protocols based on the conjugacy search problem ........... 41
4.2 Protocols based on the decomposition problem .............. 43
4.2.1 "Twisted" protocol ................................. 44
4.2.2 Hiding one of the subgroups ........................ 44
4.2.3 Commutative subgroups .............................. 45
4.2.4 Using matrices ..................................... 45
4.2.5 Using the triple decomposition problem ............. 45
4.3 A protocol based on the factorization search problem ...... 46
4.4 Stickel's key exchange protocol ........................... 47
4.4.1 Linear algebra attack .............................. 48
4.5 The Anshel-Anshel-Goldfeld protocol ....................... 50
4.6 Relations between different problems ...................... 51
Chapter 5 Platform Groups ..................................... 55
5.1 Braid groups .............................................. 55
5.1.1 A group of braids and its presentation ............. 56
5.1.2 Dehornoy handle free form .......................... 58
5.1.3 Garside normal form ................................ 59
5.2 Thompson's group .......................................... 60
5.3 Groups of matrices ........................................ 63
5.4 Small cancellation groups ................................. 65
5.4.1 Dehn's algorithm ................................... 65
5.5 Solvable groups ........................................... 65
5.5.1 Normal forms in free metabelian groups ............. 66
5.6 Artin groups .............................................. 68
5.7 Grigorchuk's group ........................................ 69
Chapter 6. More Protocols ...................................... 73
6.1 Using the subgroup membership search problem .............. 73
6.1.1 Groups of the form F/[R, R] ........................ 76
6.2 The MOR cryptosystem ...................................... 76
Chapter 7. Using Decision Problems in Public-Key
Cryptography ................................................... 79
7.1 The Shpilrain-Zapata scheme ............................... 79
7.1.1 The protocol ....................................... 80
7.1.2 Pool of group presentations ........................ 82
7.1.3 Generating random elements in finitely presented
groups ............................................. 83
7.2 Public-key encryption and encryption emulation attacks .... 85
Chapter 8. Authentication ...................................... 91
8.1 A Diffie-Hellman-like scheme .............................. 91
8.2 A Feige-Fiat-Shamir-like scheme ........................... 92
8.3 Authentication based on the twisted conjugacy problem ..... 93
8.4 Authentication from matrix conjugation .................... 94
8.4.1 The protocol, beta version ......................... 94
8.4.2 The protocol, full version ......................... 95
8.4.3 Cryptanalysis ...................................... 96
8.5 Authentication from actions on graphs, groups, or rings ... 97
8.5.1 When a composition of functions is hard-to-invert .. 97
8.5.2 Three protocols .................................... 98
8.5.3 Subgraph isomorphism .............................. 100
8.5.4 Graph homomorphism ................................ 101
8.5.5 Graph colorability ................................ 102
8.5.6 Endomorphisms of groups or rings .................. 103
8.5.7 Platform: free metabelian group of rank 2 ......... 104
8.5.8 Platform: 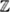 * ...................................... 104
8.6 No-leak authentication by the Sherlock Holmes method ..... 104
8.6.1 No-leak vs. zero-knowledge ........................ 105
8.6.2 The meta-protocol for authentication .............. 106
8.6.3 Correctness of the protocol ....................... 107
8.6.4 Questions and answers ............................. 108
8.6.5 Why is the Graph ISO proof system not "no-leak"? .. 109
8.6.6 A particular realization: subset sum .............. 109
8.6.7 A particular realization: polynomial equations .... 111
Part 3. Generic Complexity and Cryptanalysis
Chapter 9. Distributional Problems and the Average Case
Complexity .................................................... 117
9.1 Distributional computational problems .................... 117
9.1.1 Distributions and computational problems .......... 117
9.1.2 Stratified problems with ensembles of
distributions ..................................... 119
9.1.3 Randomized many-to-one reductions ................. 119
9.2 Average case complexity .................................. 120
9.2.1 Polynomial on average functions ................... 121
9.2.2 Average case behavior of functions ................ 125
9.2.3 Average case complexity of algorithms ............. 125
9.2.4 Average case vs. worst case ....................... 126
9.2.5 Average case behavior as a trade-off .............. 126
9.2.6 Deficiency of the average case complexity ......... 130
Chapter 10. Generic Case Complexity ........................... 131
10.1 Generic Complexity ....................................... 131
10.1.1 Generic sets ...................................... 131
10.1.2 Asymptotic density ................................ 132
10.1.3 Convergence rates ................................. 133
10.1.4 Generic complexity of algorithms and algorithmic
problems .......................................... 134
10.1.5 Deficiency of the generic complexity .............. 135
10.2 Generic versus average case complexity ................... 136
10.2.1 Comparing generic and average case complexities ... 136
10.2.2 When average polynomial time implies generic ...... 136
10.2.3 When generically easy implies easy on average ..... 138
Chapter 11. Generic Complexity of NP-complete Problems ........ 141
11.1 The linear generic time complexity of subset sum problem . 141
11.2 A practical algorithm for the subset sum problem ......... 142
11.3 3-Satisfiability ......................................... 143
Chapter 12 Generic Complexity of Undecidable Problems ........ 147
12.1 The halting problem ...................................... 147
12.2 The Post correspondence problem .......................... 150
12.3 Finitely presented semigroups with undecidable word
problem .................................................. 150
Chapter 13. Strongly, Super, and Absolutely Undecidable
Problems ...................................................... 155
13.1 Halting problem for Turing machines ...................... 157
13.2 Strongly undecidable problems ............................ 158
13.2.1 The halting problem is strongly undecidable ....... 158
13.2.2 Strongly undecidable analog of Rice's theorem ..... 159
13.3 Generic amplification of undecidable problems ............ 160
13.4 Semigroups with super-undecidable word problems .......... 163
13.5 Absolutely undecidable problems .......................... 165
Part 4. Asymptotically Dominant Properties and Cryptanalysis
Chapter 14. Asymptotically Dominant Properties ................ 171
14.1 A brief description ...................................... 171
14.2 Random subgroups and generating tuples ................... 172
14.3 Asymptotic properties of subgroups ....................... 173
14.4 Groups with generic free basis property .................. 174
14.5 Quasi-isometrically embedded subgroups ................... 176
Chapter 15 Length Based and Quotient Attacks ................. 179
15.1 Anshel-Anshel-Goldfeld scheme ............................ 179
15.1.1 Description of the Anshel-Anshel-Goldfeld scheme .. 179
15.1.2 Security assumptions of the AAG scheme ............ 179
15.2 Length based attacks ..................................... 181
15.2.1 A general description ............................. 181
15.2.2 LBA in free groups ................................ 184
15.2.3 LBA in groups from * ...................................... 104
8.6 No-leak authentication by the Sherlock Holmes method ..... 104
8.6.1 No-leak vs. zero-knowledge ........................ 105
8.6.2 The meta-protocol for authentication .............. 106
8.6.3 Correctness of the protocol ....................... 107
8.6.4 Questions and answers ............................. 108
8.6.5 Why is the Graph ISO proof system not "no-leak"? .. 109
8.6.6 A particular realization: subset sum .............. 109
8.6.7 A particular realization: polynomial equations .... 111
Part 3. Generic Complexity and Cryptanalysis
Chapter 9. Distributional Problems and the Average Case
Complexity .................................................... 117
9.1 Distributional computational problems .................... 117
9.1.1 Distributions and computational problems .......... 117
9.1.2 Stratified problems with ensembles of
distributions ..................................... 119
9.1.3 Randomized many-to-one reductions ................. 119
9.2 Average case complexity .................................. 120
9.2.1 Polynomial on average functions ................... 121
9.2.2 Average case behavior of functions ................ 125
9.2.3 Average case complexity of algorithms ............. 125
9.2.4 Average case vs. worst case ....................... 126
9.2.5 Average case behavior as a trade-off .............. 126
9.2.6 Deficiency of the average case complexity ......... 130
Chapter 10. Generic Case Complexity ........................... 131
10.1 Generic Complexity ....................................... 131
10.1.1 Generic sets ...................................... 131
10.1.2 Asymptotic density ................................ 132
10.1.3 Convergence rates ................................. 133
10.1.4 Generic complexity of algorithms and algorithmic
problems .......................................... 134
10.1.5 Deficiency of the generic complexity .............. 135
10.2 Generic versus average case complexity ................... 136
10.2.1 Comparing generic and average case complexities ... 136
10.2.2 When average polynomial time implies generic ...... 136
10.2.3 When generically easy implies easy on average ..... 138
Chapter 11. Generic Complexity of NP-complete Problems ........ 141
11.1 The linear generic time complexity of subset sum problem . 141
11.2 A practical algorithm for the subset sum problem ......... 142
11.3 3-Satisfiability ......................................... 143
Chapter 12 Generic Complexity of Undecidable Problems ........ 147
12.1 The halting problem ...................................... 147
12.2 The Post correspondence problem .......................... 150
12.3 Finitely presented semigroups with undecidable word
problem .................................................. 150
Chapter 13. Strongly, Super, and Absolutely Undecidable
Problems ...................................................... 155
13.1 Halting problem for Turing machines ...................... 157
13.2 Strongly undecidable problems ............................ 158
13.2.1 The halting problem is strongly undecidable ....... 158
13.2.2 Strongly undecidable analog of Rice's theorem ..... 159
13.3 Generic amplification of undecidable problems ............ 160
13.4 Semigroups with super-undecidable word problems .......... 163
13.5 Absolutely undecidable problems .......................... 165
Part 4. Asymptotically Dominant Properties and Cryptanalysis
Chapter 14. Asymptotically Dominant Properties ................ 171
14.1 A brief description ...................................... 171
14.2 Random subgroups and generating tuples ................... 172
14.3 Asymptotic properties of subgroups ....................... 173
14.4 Groups with generic free basis property .................. 174
14.5 Quasi-isometrically embedded subgroups ................... 176
Chapter 15 Length Based and Quotient Attacks ................. 179
15.1 Anshel-Anshel-Goldfeld scheme ............................ 179
15.1.1 Description of the Anshel-Anshel-Goldfeld scheme .. 179
15.1.2 Security assumptions of the AAG scheme ............ 179
15.2 Length based attacks ..................................... 181
15.2.1 A general description ............................. 181
15.2.2 LBA in free groups ................................ 184
15.2.3 LBA in groups from 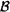 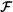 exp .......................... 185
15.3 Computing the geodesic length in a subgroup .............. 186
15.3.1 Related algorithmic problems ...................... 186
15.3.2 Geodesic length in braid groups ................... 188
15.4 Quotient attacks ......................................... 189
15.4.1 Membership problems in free groups ................ 190
15.4.2 Conjugacy problems in free groups ................. 191
15.4.3 The MSP and SCSP* in groups with "good" quotients . 194
Part 5. Word and Conjugacy Search Problems in Groups
Chapter 16. Word Search Problem ............................... 199
16.1 Introduction ............................................. 199
16.2 Presentations of groups .................................. 203
16.3 Approximating Cayley graphs of finitely presented groups . 204
16.3.1 Cayley graph approximations and singular
subcomplexes ...................................... 204
16.3.2 van Kampen diagrams ............................... 208
16.3.3 Depth of diagrams and the canonical embeddings .... 209
16.4 New algorithms for the word search problem in groups ..... 212
16.4.1 Search problems in groups ......................... 212
16.4.2 The word search problem in groups. Algorithm exp .......................... 185
15.3 Computing the geodesic length in a subgroup .............. 186
15.3.1 Related algorithmic problems ...................... 186
15.3.2 Geodesic length in braid groups ................... 188
15.4 Quotient attacks ......................................... 189
15.4.1 Membership problems in free groups ................ 190
15.4.2 Conjugacy problems in free groups ................. 191
15.4.3 The MSP and SCSP* in groups with "good" quotients . 194
Part 5. Word and Conjugacy Search Problems in Groups
Chapter 16. Word Search Problem ............................... 199
16.1 Introduction ............................................. 199
16.2 Presentations of groups .................................. 203
16.3 Approximating Cayley graphs of finitely presented groups . 204
16.3.1 Cayley graph approximations and singular
subcomplexes ...................................... 204
16.3.2 van Kampen diagrams ............................... 208
16.3.3 Depth of diagrams and the canonical embeddings .... 209
16.4 New algorithms for the word search problem in groups ..... 212
16.4.1 Search problems in groups ......................... 212
16.4.2 The word search problem in groups. Algorithm 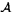 exp . 213
16.4.3 The word search problem in groups. Algorithm exp . 213
16.4.3 The word search problem in groups. Algorithm 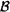 exp . 215
16.5 Random van Kampen diagrams ............................... 218
16.5.1 Basic random extensions and simple random walks ... 218
16.5.2 Probability and asymptotic measure on diagrams .... 219
16.5.3 Iterative random generator RGn .................... 222
16.5.4 Diagram complexity and random generator RGX ....... 222
16.6 Basic extension algorithm Bs and relative probability
measures ................................................. 224
16.6.1 Basic extension BS ................................ 224
16.6.2 Completeness of the basic extension BS ............ 226
16.6.3 Some properties of BS ............................. 236
16.7 Asymptotic properties of diagrams ........................ 237
16.7.1 Properties related to RGX ......................... 237
16.8 Generic properties of trivial words ...................... 242
16.8.1 Random trivial words .............................. 242
16.8.2 Generic properties of trivial words ............... 243
16.9 Comparison with standard techniques ...................... 245
16.9.1 The Todd-Coxeter algorithm ........................ 245
16.9.2 Total enumeration of GPF(R) ....................... 246
Chapter 17. Conjugacy Search Problem .......................... 247
17.1 Introduction ............................................. 247
17.2 Weighted graphs .......................................... 248
17.2.1 Definition ........................................ 248
17.2.2 Conjugacy and pseudo conjugacy graphs ............. 249
17.3 Transformations of weighted X-digraphs ................... 250
17.3.1 Shift operator .................................... 251
17.3.2 Staffings' fold ................................... 252
17.3.3 Staffings' procedure .............................. 254
17.3.4 Basic extension ................................... 256
17.3.5 Д-extension algorithm ............................. 258
17.4 Conjugacy graphs ......................................... 259
17.4.1 Existence of conjugacy graphs ..................... 260
17.4.2 Conjugacy graph approximation ..................... 261
17.5 Annular (Schupp) diagrams ................................ 262
17.5.1 Depth of annular diagrams ......................... 263
17.5.2 Annular diagrams as pseudo conjugacy graphs ....... 264
17.6 The conjugacy search problem ............................. 264
17.6.1 Annular diagram bisection ......................... 264
17.6.2 Conjugacy search algorithm ........................ 269
17.7 Random annular diagrams .................................. 272
17.7.1 Basic random extension of annular diagrams ........ 274
17.7.2 Completeness of BS ................................ 278
17.8 Asymptotic properties of random annular diagrams ......... 279
17.9 Asymptotic properties of conjugated words ................ 280
17.9.1 Random conjugated words ........................... 280
17.9.2 Generic properties of random conjugated words .. 281
Part 6. Word Problem in some Special Classes of Groups
Chapter 18. Free Solvable Groups .............................. 285
18.1 Preliminaries ............................................ 289
18.1.1 The word problem .................................. 289
18.1.2 Free solvable groups and the Magnus embedding ..... 289
18.1.3 Free Fox derivatives .............................. 291
18.1.4 Flows on F/N ...................................... 292
18.1.5 Geometric interpretation of Fox derivatives ....... 294
18.1.6 Geometric circulations and the first homology
group of Г ........................................ 296
18.1.7 Geodesies in F/N1 ................................. 296
18.2 The word problem in free solvable groups ................. 298
18.2.1 The word problem in free metabelian groups ........ 298
18.2.2 The word problem in free solvable groups .......... 300
18.3 Geodesies in free metabelian groups ...................... 303
18.3.1 Algorithmic problems about geodesies in groups .... 303
18.3.2 Reduction to M2 ................................... 304
18.3.1 Rectilinear Steiner tree problem .................. 305
18.3.4 NP-completeness of BGLP in M2 ..................... 305
Chapter 19. Compressed Words .................................. 309
19.1 Straight line programs ................................... 309
19.2 Basic operations over SLPs ............................... 310
19.2.1 Subwords .......................................... 310
19.2.2 Inversion ......................................... 312
19.3 Plandowski's algorithm ................................... 312
19.3.1 Assertions ........................................ 312
19.3.2 Trimming .......................................... 314
19.3.3 Splitting ......................................... 315
19.3.4 Compactification .................................. 316
19.3.5 Satisfiability of SLP ............................. 318
19.3.6 Plandowski's algorithm ............................ 319
19.4 Longest common initial segment ........................... 319
19.5 Reduction ................................................ 320
19.6 The word problem in the automorphism group of a free
group .................................................... 321
Appendix A. Probabilistic Group-based Cryptanalysis ........... 325
A.l Introduction ............................................. 325
A.2 Probability theory on groups ............................. 328
A.2.1 Probabilities for various spaces - overview ....... 328
A.2.2 Mean (expectation) of a group-valued random
element ........................................... 331
A.2.3 The mean set in a group ........................... 333
A.2.4 Other possible definitions of exp . 215
16.5 Random van Kampen diagrams ............................... 218
16.5.1 Basic random extensions and simple random walks ... 218
16.5.2 Probability and asymptotic measure on diagrams .... 219
16.5.3 Iterative random generator RGn .................... 222
16.5.4 Diagram complexity and random generator RGX ....... 222
16.6 Basic extension algorithm Bs and relative probability
measures ................................................. 224
16.6.1 Basic extension BS ................................ 224
16.6.2 Completeness of the basic extension BS ............ 226
16.6.3 Some properties of BS ............................. 236
16.7 Asymptotic properties of diagrams ........................ 237
16.7.1 Properties related to RGX ......................... 237
16.8 Generic properties of trivial words ...................... 242
16.8.1 Random trivial words .............................. 242
16.8.2 Generic properties of trivial words ............... 243
16.9 Comparison with standard techniques ...................... 245
16.9.1 The Todd-Coxeter algorithm ........................ 245
16.9.2 Total enumeration of GPF(R) ....................... 246
Chapter 17. Conjugacy Search Problem .......................... 247
17.1 Introduction ............................................. 247
17.2 Weighted graphs .......................................... 248
17.2.1 Definition ........................................ 248
17.2.2 Conjugacy and pseudo conjugacy graphs ............. 249
17.3 Transformations of weighted X-digraphs ................... 250
17.3.1 Shift operator .................................... 251
17.3.2 Staffings' fold ................................... 252
17.3.3 Staffings' procedure .............................. 254
17.3.4 Basic extension ................................... 256
17.3.5 Д-extension algorithm ............................. 258
17.4 Conjugacy graphs ......................................... 259
17.4.1 Existence of conjugacy graphs ..................... 260
17.4.2 Conjugacy graph approximation ..................... 261
17.5 Annular (Schupp) diagrams ................................ 262
17.5.1 Depth of annular diagrams ......................... 263
17.5.2 Annular diagrams as pseudo conjugacy graphs ....... 264
17.6 The conjugacy search problem ............................. 264
17.6.1 Annular diagram bisection ......................... 264
17.6.2 Conjugacy search algorithm ........................ 269
17.7 Random annular diagrams .................................. 272
17.7.1 Basic random extension of annular diagrams ........ 274
17.7.2 Completeness of BS ................................ 278
17.8 Asymptotic properties of random annular diagrams ......... 279
17.9 Asymptotic properties of conjugated words ................ 280
17.9.1 Random conjugated words ........................... 280
17.9.2 Generic properties of random conjugated words .. 281
Part 6. Word Problem in some Special Classes of Groups
Chapter 18. Free Solvable Groups .............................. 285
18.1 Preliminaries ............................................ 289
18.1.1 The word problem .................................. 289
18.1.2 Free solvable groups and the Magnus embedding ..... 289
18.1.3 Free Fox derivatives .............................. 291
18.1.4 Flows on F/N ...................................... 292
18.1.5 Geometric interpretation of Fox derivatives ....... 294
18.1.6 Geometric circulations and the first homology
group of Г ........................................ 296
18.1.7 Geodesies in F/N1 ................................. 296
18.2 The word problem in free solvable groups ................. 298
18.2.1 The word problem in free metabelian groups ........ 298
18.2.2 The word problem in free solvable groups .......... 300
18.3 Geodesies in free metabelian groups ...................... 303
18.3.1 Algorithmic problems about geodesies in groups .... 303
18.3.2 Reduction to M2 ................................... 304
18.3.1 Rectilinear Steiner tree problem .................. 305
18.3.4 NP-completeness of BGLP in M2 ..................... 305
Chapter 19. Compressed Words .................................. 309
19.1 Straight line programs ................................... 309
19.2 Basic operations over SLPs ............................... 310
19.2.1 Subwords .......................................... 310
19.2.2 Inversion ......................................... 312
19.3 Plandowski's algorithm ................................... 312
19.3.1 Assertions ........................................ 312
19.3.2 Trimming .......................................... 314
19.3.3 Splitting ......................................... 315
19.3.4 Compactification .................................. 316
19.3.5 Satisfiability of SLP ............................. 318
19.3.6 Plandowski's algorithm ............................ 319
19.4 Longest common initial segment ........................... 319
19.5 Reduction ................................................ 320
19.6 The word problem in the automorphism group of a free
group .................................................... 321
Appendix A. Probabilistic Group-based Cryptanalysis ........... 325
A.l Introduction ............................................. 325
A.2 Probability theory on groups ............................. 328
A.2.1 Probabilities for various spaces - overview ....... 328
A.2.2 Mean (expectation) of a group-valued random
element ........................................... 331
A.2.3 The mean set in a group ........................... 333
A.2.4 Other possible definitions of 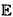 .................. 334
A.3 Strong law of large numbers .............................. 334
A.3.1 Separation and inclusion lemmas ................... 336
A.3.2 Case of multi-vertex mean-sets .................... 339
A.4 Concentration of measure inequalities .................... 345
A.4.1 Chebyshev's inequality for graphs/groups .......... 345
A.4.2 Chernoff-Hoeffding-like bound for graphs/groups ... 348
A.5 Configurations of mean-sets .............................. 349
A.6 Computation of mean-sets in graphs ....................... 352
A.6.1 Experiments ....................................... 353
A.7 Probabilistic cryptanalysis of Sibert type protocols ..... 354
A.7.1 Outline ........................................... 355
A.7.2 Zero-knowledge interactive proof systems .......... 355
A.7.3 Description of the protocol ....................... 356
A.7.4 Security of the protocol .......................... 357
A.7.5 The idea of mean-set attack: the shift search
problem ........................................... 358
A.7.6 Effective computation of a mean-set ............... 359
A.7.7 The mean-set attack ............................... 360
A.7.8 Experiments ....................................... 363
A.7.9 Defending against the attack ...................... 366
Bibliography .................................................. 369
Abbreviations and Notation .................................... 381
Index ......................................................... 383 .................. 334
A.3 Strong law of large numbers .............................. 334
A.3.1 Separation and inclusion lemmas ................... 336
A.3.2 Case of multi-vertex mean-sets .................... 339
A.4 Concentration of measure inequalities .................... 345
A.4.1 Chebyshev's inequality for graphs/groups .......... 345
A.4.2 Chernoff-Hoeffding-like bound for graphs/groups ... 348
A.5 Configurations of mean-sets .............................. 349
A.6 Computation of mean-sets in graphs ....................... 352
A.6.1 Experiments ....................................... 353
A.7 Probabilistic cryptanalysis of Sibert type protocols ..... 354
A.7.1 Outline ........................................... 355
A.7.2 Zero-knowledge interactive proof systems .......... 355
A.7.3 Description of the protocol ....................... 356
A.7.4 Security of the protocol .......................... 357
A.7.5 The idea of mean-set attack: the shift search
problem ........................................... 358
A.7.6 Effective computation of a mean-set ............... 359
A.7.7 The mean-set attack ............................... 360
A.7.8 Experiments ....................................... 363
A.7.9 Defending against the attack ...................... 366
Bibliography .................................................. 369
Abbreviations and Notation .................................... 381
Index ......................................................... 383
|